Kubernetes
Kubernetes is an opensource orchestrator allowing to automate the deployment, scaling and management of containerized applications. Also named k8s the 8 for the eight letters in “ubernete” plus “s”.
It was originally developed by Google in Go. Kubernetes means “Helmsman” the guy who holds “Governor” in greek. Let’s get sailing!
Helm
With Kubernetes, you have Helm which act as the packet manager for kubernetes.
Helm comes with charts that allow oneself to deploy a certain cluster with a single command line.
Most of the charts are community maintained, they help define, install and define the application. They work using
template with values that can then be changed easily in one place the values.yml file.
Components High-level
Application from Container to Pods
The containerized application is available on multiple replica containers. These containers are regrouped by ** Pods**.
On a worker there are multiple pods. A worker is a high level application block in Kubernetes.
The worker can have interaction with the outisde of thanks to an ingress node which act as a proxy for everything coming in. The worker can also interact with the outside, by sending information and else using an egress node which act as a reverse proxy for external outgoing communication.
Node Overview
A minion or a node is where the worker machine is situated. It includes the services for Docker (container), ** Kubelet** (management) and Kubeproxy (network).
The kubelet is the primary “node agent” that runs on each node. The kubelet works in terms of a PodSpec. A PodSpec is a YAML or JSON object that describes a pod. It then makes sure that the pods described by the PodSpec are healthy.
The Kubernetes network proxy or kubeproxy runs on each node, it is defined in the Cluster and tells how and through which ports the docker can in the pods can communicate.
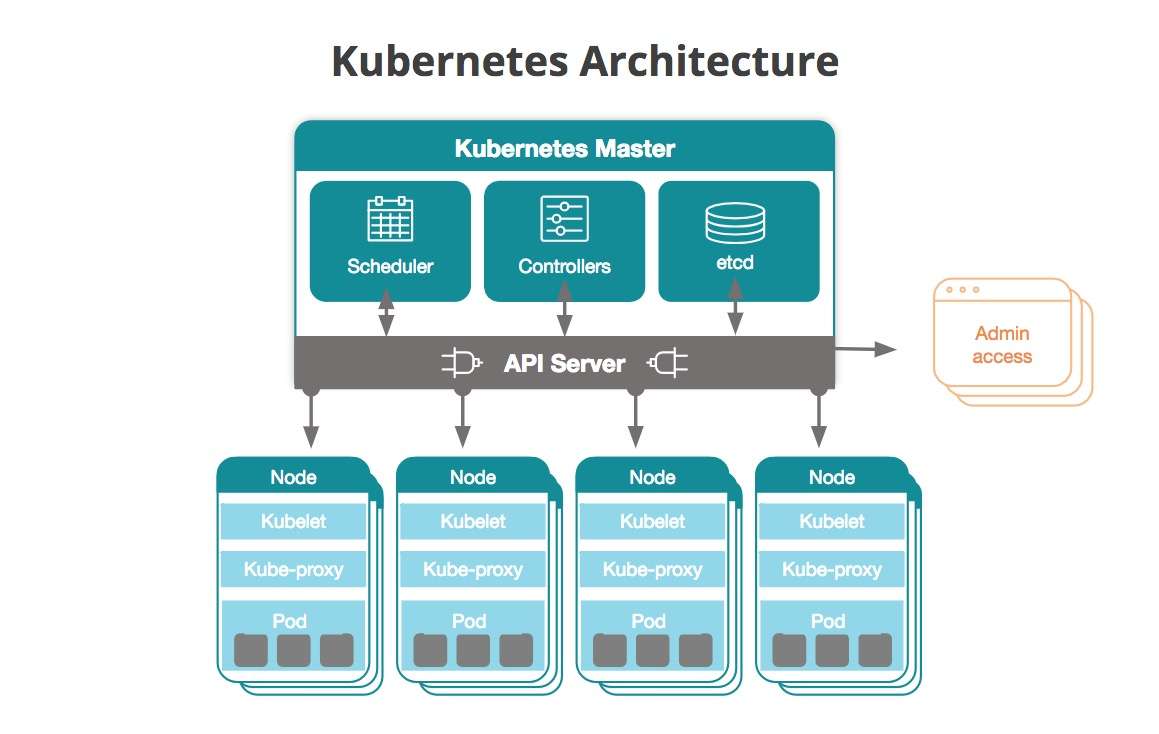
Kubernetes Cluster
A cluster is a group of worker nodes controlled by a master node which controls the replication and the management of the worker nodes.
All the nodes of the cluster uses etcd, the backend for service discovery which stores cluster state and configuration.
The kubernetes API server is a front head and a REST API for the etcd backend.
The cluster as a cli name kubectl which allow controlling and get information on the Cluster.
# Show Mmrged kubeconfig settings.
kubectl config view
Sources
Mostly the kubernetes website.